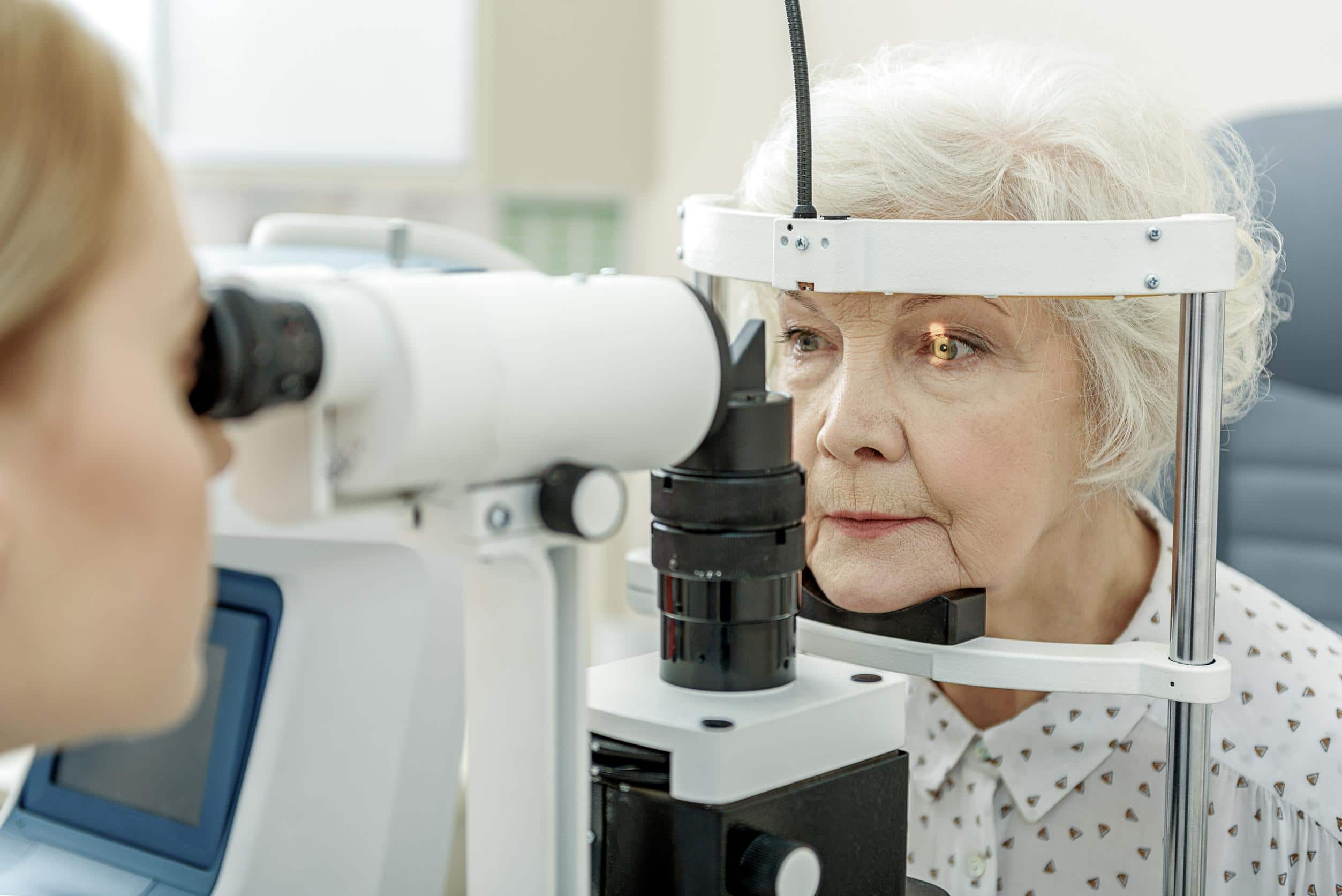
Eye Health
Common Eye Conditions
Maintaining good eye health is essential as we age. Here we look at some of the most common eye health conditions and their symptoms, causes and treatment options. If you have any concerns about any aspect of your vision or eye health, give us a call today and book an eye health check.


Child myopia
Myopia is a common vision condition in children and teenagers, where light is focused in front of the retina resulting in blurred distance vision – also known as near or short-sightedness. This means your child will be able to see things clearly up close, such as a book they’re reading, and have difficulty seeing things further away such as a whiteboard at the front of the classroom. Myopia usually starts in childhood, worsening as the child grows into a teenager. While there is no cure, early detection and treatment can help slow and control the progression.
SYMPTOMS Sore or tired eyes, headaches, squinting or increased concentration.
TREATMENT Myopia control options include: MiyoSmart® spectacle lenses, soft contact lenses such as MiyoSmart® and Ortho-K, as well as Atropine, a compounded eye drop application.
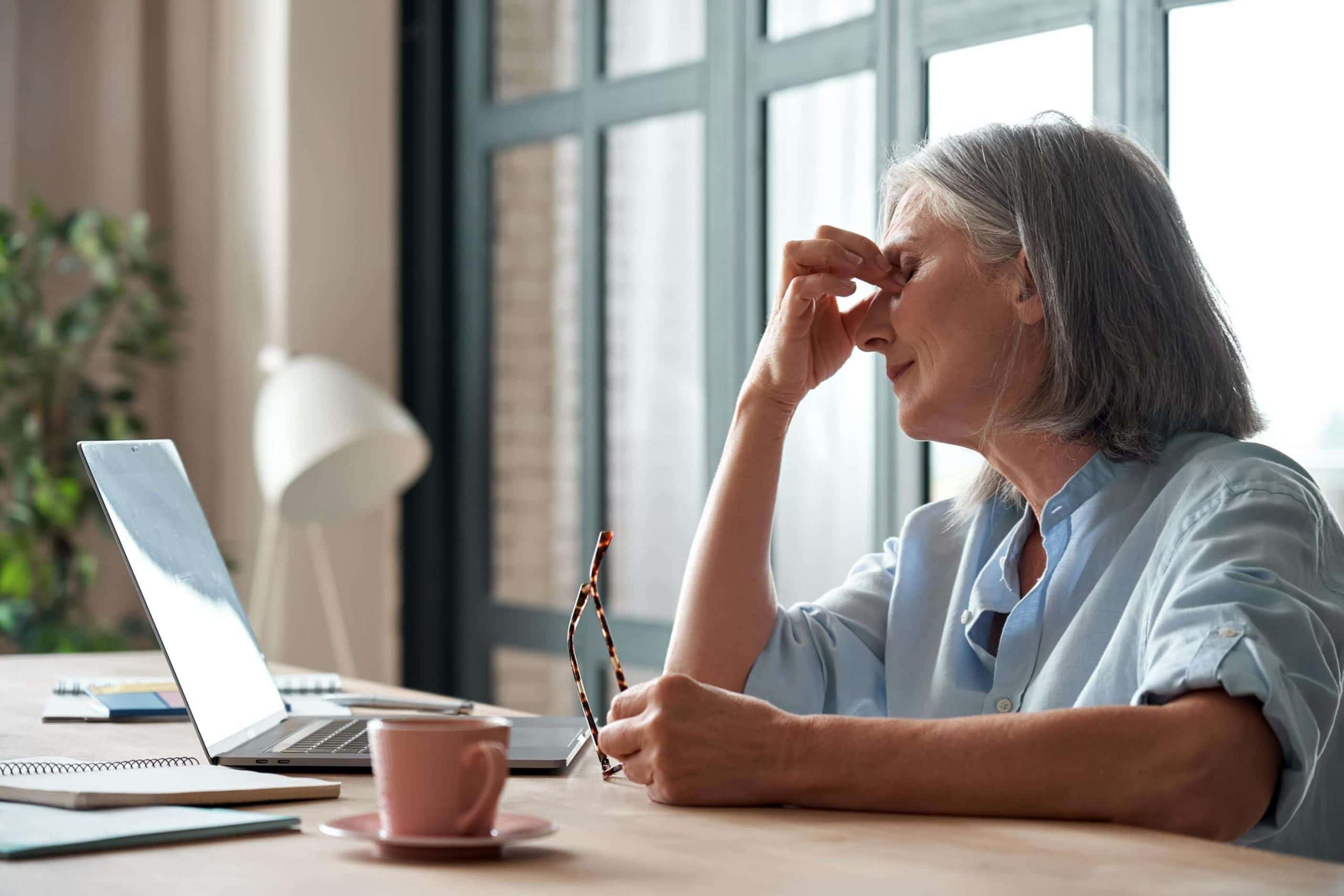

Dry Eyes
Dry eyes is a common condition affecting one in five adults, where there isinadequate moisture or natural lubrication for the eyes – there may be an insufficient supply of tears or tears evaporate too quickly. A chronic condition, dry eyes can have a significant impact on your daily life. Ongoing treatment is required to help relieve symptoms, however there
SYMPTOMS Sore, itchy or irritated eyes, similar to the feeling of having a foreign object in the eye. Fluctuation in vision. Trouble reading or watching a screen.
TREATMENT Treatment options include lifestyle changes as well as eye drops, gels or ointments, also known as artificial tears.
Glaucoma
A leading cause of blindness in Australia, Glaucoma is a common eye disease that
tends to run in families, where peripheral vision is lost due to damage to the optic nerve, connecting the eye to the brain. This is usually caused by a build-up of pressure in the eye (intraocular pressure), due to a blockage in the eye’s drainage system. While there is no cure, and damage cannot be reversed, early detection and treatment can slow or minimise vision loss.
SYMPTOMS Gradual loss of peripheral vision. Often there are no obvious symptoms until the optic nerve is damaged so regular eye check ups are essential.
TREATMENT Treatment involves lowering the pressure in the eye, and may include eye drops, laser treatment or surgery.
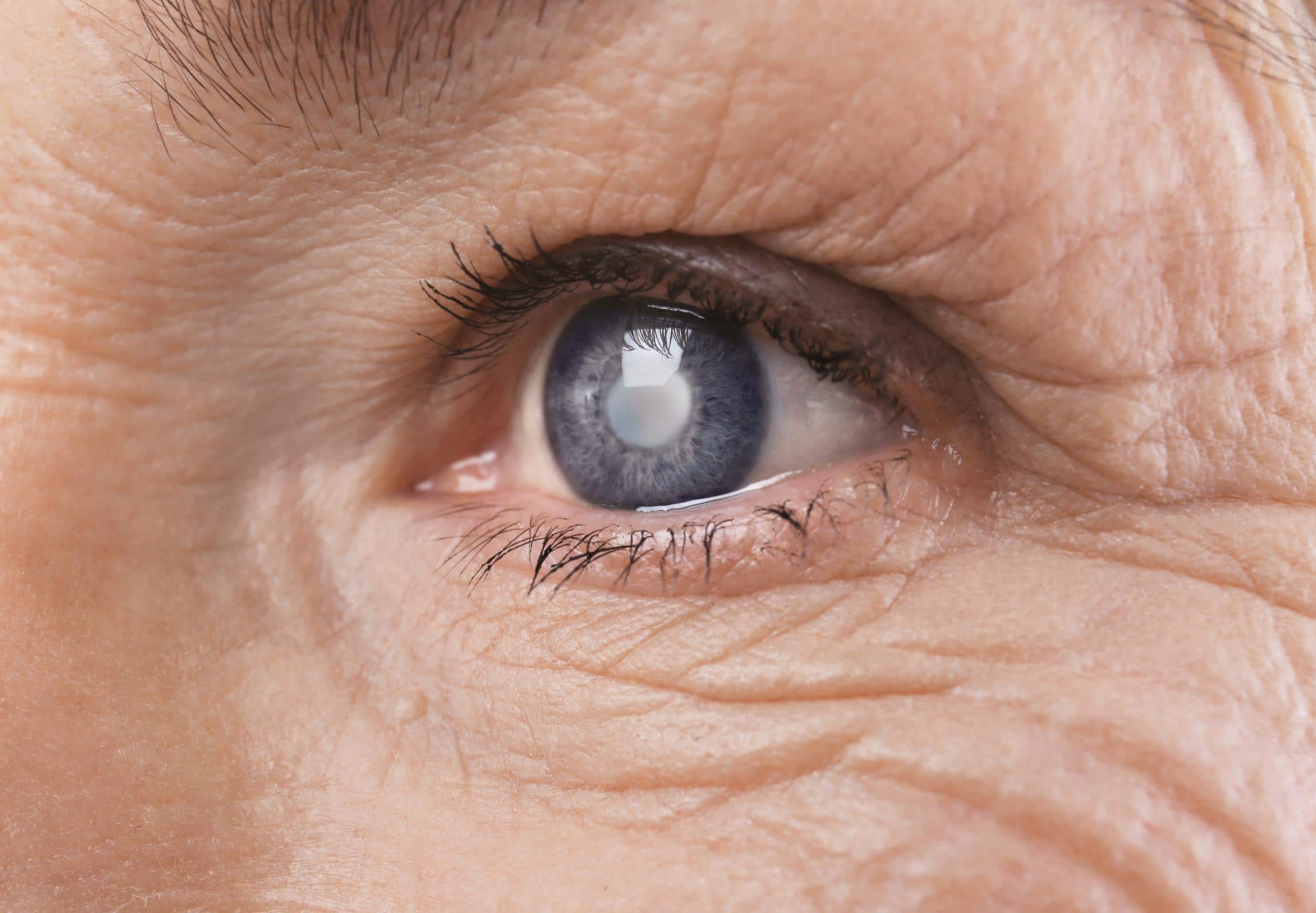
Cataracts
Cataracts are a clouding of the lens of the eye, resulting in blurry vision, and are a
major cause of blindness in adults worldwide. Although mostly common with older people, younger people as well as babies can also develop cataracts. Risk factors for cataracts include older age, smoking, diabetes, family history or too much sun exposure. Most cataracts develop slowly over the course of years, but in most cases can be successfully treated and vision restored.
SYMPTOMS Blurry, distorted or double vision, sensitivity to light or seeing halos around lights, difficulty reading or driving at night.
TREATMENT Treatment involves removing the cloudy lens in a surgical procedure.
Diabetic retinopathy
SYMPTOMS Gradual or sudden loss of vision, blurry vision, spots or floaters in vision.
TREATMENT Management of diabetes, blood pressure and cholesterol through diet and lifestyle changes, as well as laser treatments and surgery.

Macular degeneration
Macular degeneration is an eye disease that causes vision loss in the centre of your
field of vision, due to the deterioration of the macula (part of the retina at the back of the eye). More common in people aged 50 years and over, it’s often referred to as age-related macular degeneration or AMD. The cause is not known, however genetic and lifestyle factors may play a part. As with many common eye conditions, the earlier the disease is detected, the better the outcome. However, while treatment can help reduce your risk or slow down vision loss, there is no cure.
SYMPTOMS Partial loss of central vision, blurry or wavy areas in your vision, difficulty reading or driving at night even with glasses.
TREATMENT Certain supplements as well as diet and lifestyle changes may help slow down the disease progression. Depending on the type of AMD you have, medication, laser treatments and surgery may also be an option.




